The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is a US federal agency that sets standards for safe working conditions. OSHA’s standards are highly regarded and used to set organizational benchmarks all over the world. In this article, we look at OSHA’s five most-cited standards and how digitalization can help your organization stay compliant with them.
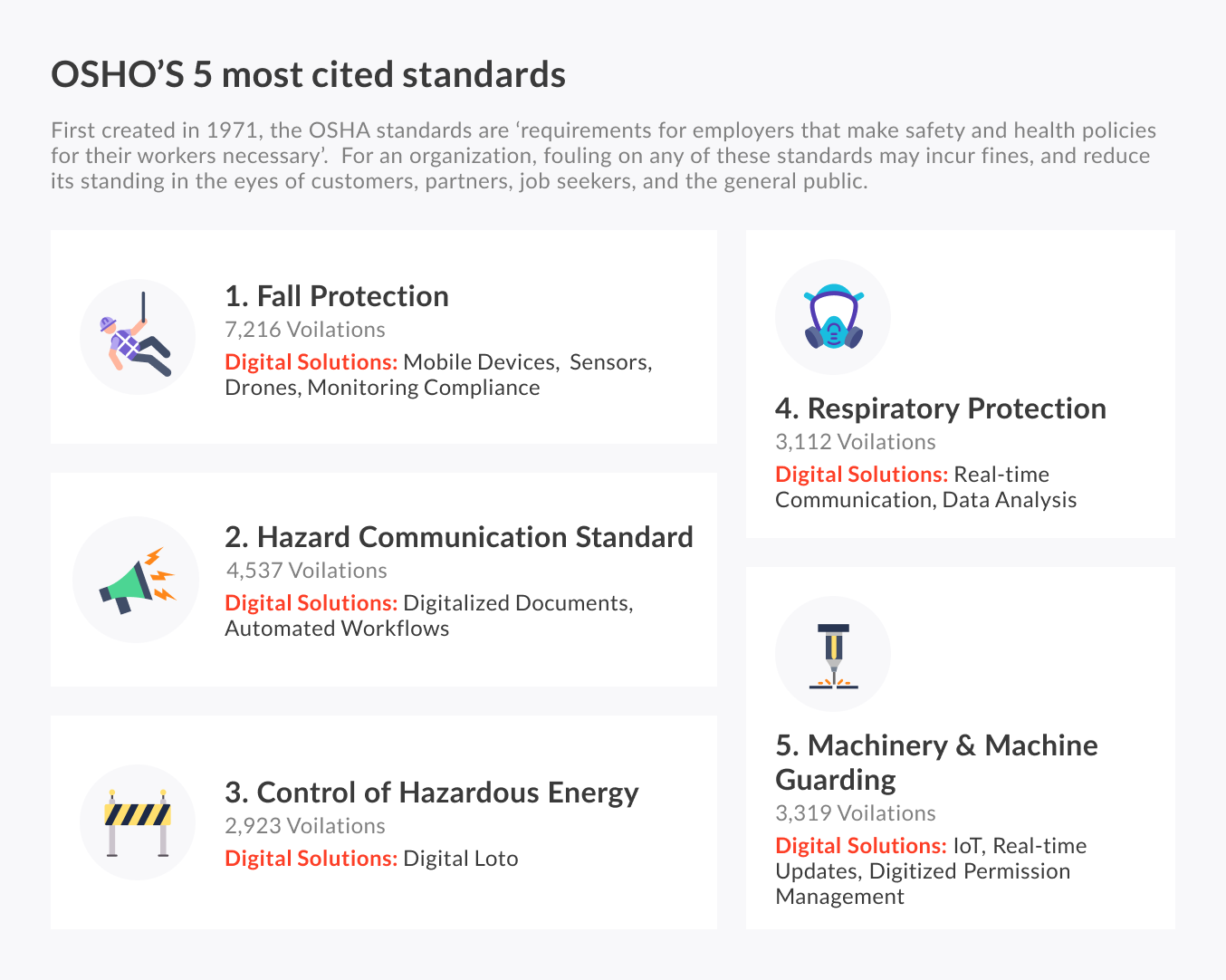
First created in 1971, the OSHA standards are ‘requirements for employers that make safety and health policies for their workers necessary’. For an organization, fouling on any of these standards may incur fines, and reduce its standing in the eyes of customers, partners, job seekers, and the general public.
Fortunately, digital technology can take the pressure off and equip enterprises to better safeguard their workplaces.
OSHA’S 5 most cited standards:
- Fall protection
- Hazard communication standard
- Control of hazardous energy (logout/ tag out)
- Respiratory protection
- Machinery and machine guarding
Now let’s look at each of these in detail and understand how digitalization can ensure compliance.
Fall protection, construction (29 CFR 1926.501)
In 2018, 338 out of 1008 total deaths in construction were from falls (33.5%) – Bureau of Labour Statistics.
- Mobile Devices: Using mobile triggers (on hand-held devices like a smartphone or tablet), workers can tap a ‘panic’ button to send distress calls to line managers before and after falls. In the case that a worker does not have enough time to hit the button, the accelerometer on their mobile phones will pick up the anomaly caused by the fall and send automatic mobile alerts to call for emergency help.
- Sensors: Employees who often work at heights can have their balance regularly tested with ‘smart slippers’. These shoes with built-in sensors can gauge their stability in real-time and provide data for managers who can then chart the progressive decline in stability and quickly identify those at risk of falls.
- Drones: At extreme heights and in difficult terrains/hazardous environments, drones can be used to conduct remote inspections – without putting employees in harm’s way. Camera-fitted drones can also be used to monitor security in sensitive remote areas and conduct virtual walk-throughs where practical safety training can be organized for employees.
- Monitoring Compliance: Through digital inspections and audits, managers can remotely monitor the work environment and have real-time visual oversight of areas where falls may be likely. This will help them take proactive measures to safeguard their workers and send emergency help in the case of an accident.
Hazard communication standard, general industry (29 CFR 1910.1200)
OSHA’s updated hazard communication standard covers over 650,000 hazardous chemical products and 43 million workers in 5 million workplaces across the US.
- Digitized Documents: Digital safety data is easier to disseminate and understand, a personalized and less cumbersome hazard communication standard can be shared to stakeholders across the shop floor. It can be customized in multiple languages and font sizes to accommodate all employees.
- Automated Workflows: Additionally, digital auto-updates can be sent to stakeholders to pass across necessary (and updated standard information) in a timely manner. The consequence will be greater employee awareness of hazardous chemicals which will improve their handling and prevent top release in the workplace.
Control of hazardous energy (lockout/tag out), general industry (29 CFR 1910.147)
Proper Lockout / Tagout (LOTO) procedures to control hazardous energy prevent 120 fatalities and 50,000 injuries each year – OSHA
- Digital LOTO: Digital technologies have paved the way for stakeholders to have access to an electronic LOTO procedure which is easier to utilize and can be shared with the click of a button.
An electronic LOTO procedure with visual search bars and QR code scanners can be used to quickly access the correct procedures for specific machinery.
Moreover, LOTO software can be installed on mobile phones and digital devices to provide step by step guidance through every stage of the LOTO procedure. Digital factsheets are available on the software from where employees can acknowledge that the energy source has been isolated using appropriate lockout devices. This will foster a culture of compliance and accountability as the identities of employees performing the LOTO can be entered with accompanying digital time-stamp records.
Respiratory protection, general industry (29 CFR 1910.134)
- Real-time Communication: Digitalization can help managers to better enforce workplace health and safety compliance with 24/7 live monitoring of high-risk areas. By sending real-time nudges to mobile devices, employees can be reminded to use personal protective respiratory equipment. Reminders can also be sent to notify the maintenance team of pre-scheduled or impromptu PPE maintenance and workplace decontamination.
- Data Analysis: Data from insufficient oxygen environments or hazardous working conditions can be analyzed with digital platforms to gain insight and take steps to better protect the workers.
Machinery and Machine Guarding, general requirements (29 CFR 1910.212)
In 2019, OSHA issued 1743 machine safeguarding violations.
- IoT: Sensors can be fitted to machines and connected to mobile devices for remote control of machines. This is particularly important for cases where the knowledge of the operating procedure of the machine is limited to a select few within the organization. Also, mobile alerts can be programmed to detect overtime run hours in case a manager forgets to turn off a machine before signing off.
- Real-time Updates: Machine guarding can be enhanced with real-time machine data that can be used for analysis and to pre-empt machine maintenance.
- Digitized Permission Management: Digitalization reduces the time lag in ratifying permit-to-work for external machine maintenance/repairs. With mobile permit-to-work, permits can be issued to contractors on-site by managers in remote locations. The contractor’s qualifications can be digitally assessed to determine their suitability in handling the mechanical asset.
In conclusion, human error remains the largest contributing factor to workplace accidents in the world. For this reason, the importance of quality training in safeguarding your workers and ensuring compliance with OSHA’s standard cannot be over-emphasized. OSHA has recognized this and through their Global Occupational Safety and Health Academy, LLC (Global OSHA) platform have given enterprises the opportunity to organize quality occupational safety and health programs for their employees. Global OSHA is conducted… digitally.




